자 왔다…
결국 우리가 원하는건 expected return을 최대화 할 수 있는 theta를 찾는 것이다.
결과적으로 우리가 원하는 부분은 어떤 정책을 이용해서 결과 값으로 어떤 확률을 가지는 policy를 찾는 것이다. 어떤 상황에서 특정한 확률(편향)을 가질 상황을 action preference라고 한다.
이러한 게임을 보게 되면 미래의 상황에도 좋을 선택을 하는 것이다.
그럼 어케 weight을 업데이트 하누?
기본적인 idea는 agent가 episode동안 환경과 계속 interact하게 하는 것이다. 그리고 만약 agent가 episode에서 이긴다면 해당 action들은 이기는 것에 훨씬 유의미 하다고 판단할 수 있고 미래의 episode에 더 sampling되는 것이 유리하다고 판단 할수 있다.
결과적으로 우리는 각각의 state-action pair에 대해서 P(a|s)를 늘리는 것이 목표가 된다.
아래는 presudo code인다.
policy gradient algorithm
Training Loop collect an episode with the policy Calculate the sum of reward Update the weight of the policy if positive return -> increase the probability of each (state, action) pairs taken during the episode if negative return -> decrease the probability of each (state, action) pairs taken during the episode
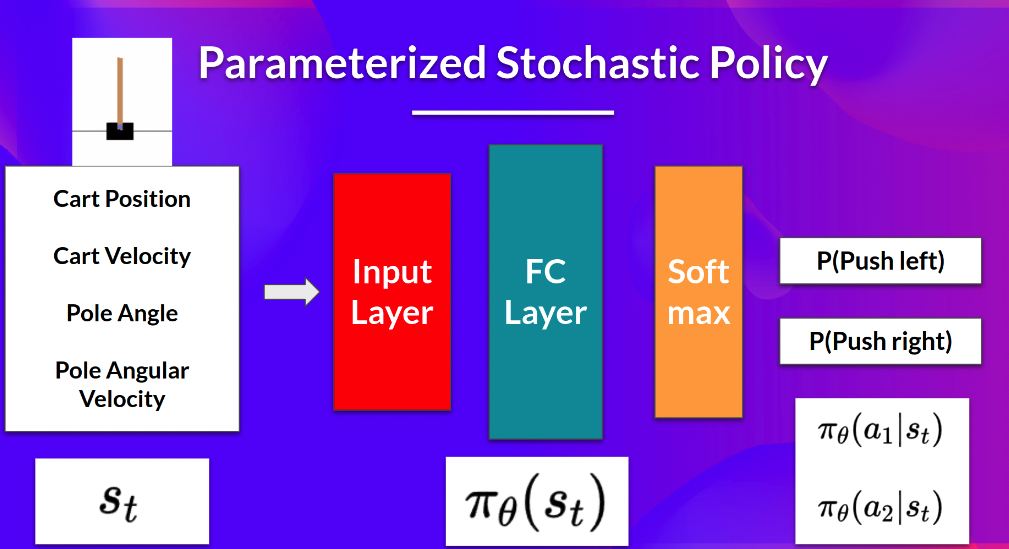
Stochastic Policy
특정 state에 대한 policy는 weight에 따른 현재 state에서의 action의 확률로 나타난다.
그렇다면 어떤 policy가 과연 좋은 걸까? 뭘 선택해야 이길 수 있냐 이말이다!
여기서는 이를 측정하기위해서 score/objective function이라는 개념을 이야기한다.
Objective function
수식의 위처럼 정의 되는데 score/objective function은 모든 reward에 discount rate을 곱한것과 같다. 이수식은 좀더 디테일하게 쓰게 되면 아래와 같게 된다.
이말을 결국 우리가 알고 싶은 policy의 좋냐는 것을 측정할 수 있는 score/objective function은 기대하는 혹은 누적된 모든 reward에 대한 가중평균을 의미한다.
Maximize the Objective function
결국 우리는 J(theta)를 최대화 하는 weight(theta)를 찾는게 목표다
이는 아래와 같은 수식으로 theta를 업데이트 할 것이다.
여기에는 2가지 문제가 존재한다.
- 첫번째는 한 epoch마다 모든 cumulative reward를 계산하는 것은 매우 비용이 많이 든다. 따라서 우리는 sample-based estimate를 통해 기울기를 근사할 것이다.
- (We have another problem that I explain in the next optional section. To differentiate this objective function, we need to differentiate the state distribution, called the Markov Decision Process dynamics. This is attached to the environment. It gives us the probability of the environment going into the next state, given the current state and the action taken by the agent. The problem is that we can’t differentiate it because we might not know about it.) 라는 데 잠시 대기
policy gradient theorem에 의해서 나온 두번째 문재를 해결할 예정이다.
policy gradient theorem
The reinforce algorithm (Monte Carlo Reinforce)
rl 알고리즘은 다움과 같은 순서를 가진다.
loop: policy를 이용해서 episode를 collecting한다. episode의 cumulated reward의 기울기 (gradient)를 구한다. theta를 업데이트 한다. * 여기서 log pi부분은 t시점에서 policy에 의해 action을 선택할 경우의 가능성인데 * 이에 대한 gradient 개념은 해당 시점에서 가장 가파르게 움직일 수 있는 방향성을 의미한다. * 만약 결과 값이 크다면 확률을 높일 것이고 값이 낮다면 가능성을 낮출 것이다.
자 과연 누가 얼마나 알고 있을 것 인가??? 어디한번 예시를 들어보자